算法
约 4642 字大约 15 分钟
2025-06-20
数据结构
基础数据结构
背包
/**
* 背包
*/
public class Bag<Item> implements Iterable<Item> {
private Node first;
private int N; // 维护背包中元素的数量
private class Node {
Item item;
Node next;
}
/**
* 添加元素到背包头部
* @param item 要添加的元素
*/
public void add(Item item) {
Node oldfirst = first;
first = new Node();
first.item = item;
first.next = oldfirst;
N++; // 元素数量加一
}
/**
* 删除背包头部的元素
* @return 被删除的元素
* @throws NoSuchElementException 如果背包为空
*/
public Item remove() throws NoSuchElementException {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new NoSuchElementException("Bag is empty");
}
Item item = first.item; // 获取头部元素
first = first.next; // 移动头指针到下一个节点
N--; // 元素数量减一
return item; // 返回被删除的元素
}
/**
* 检查背包是否为空
* @return 如果背包为空则返回 true,否则返回 false
*/
public boolean isEmpty() {
return first == null;
}
/**
* 获取背包中元素的数量
* @return 元素的数量
*/
public int size() {
return N;
}
@Override
public Iterator<Item> iterator() {
return new ListIterator();
}
private class ListIterator implements Iterator<Item> {
private Node current = first;
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return current != null;
}
@Override
public Item next() {
if (!hasNext()) {
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
Item item = current.item;
current = current.next;
return item;
}
}
}定容栈
/**
* 定容栈
*/
public class FixedCapacityStack<Item> {
private Item[] a;
private int N;
public FixedCapacityStack(int cap) {
a = (Item[]) new Object[cap];
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return N == 0;
}
public int size() {
return N;
}
public void push(Item item) {
if (N == a.length) {
resize(2 * a.length);
}
a[N++] = item;
}
public Item pop() {
Item item = a[--N];
a[N] = null; // 游离对象
if (N > 0 && N == a.length / 4) {
resize(a.length/2);
}
return item;
}
private void resize(int max) {
Item[] temp = (Item[]) new Object[max];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i ++) {
temp[i] = a[i];
}
a = temp;
}
}下压栈(数组实现)
/**
* 下压栈(数组实现)
*/
public class ResizingArrayStack<Item> {
private Item[] a = (Item[]) new Object[1];
private int N;
public boolean isEmpty() {
return N == 0;
}
public int size() {
return N;
}
private void resize(int max) {
Item[] temp = (Item[]) new Object[max];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i ++) {
temp[i] = a[i];
}
a = temp;
}
public void push(Item item) {
if (N == a.length) {
resize(2 * a.length);
}
a[N++] = item;
}
public Item pop() {
Item item = a[--N];
a[N] = null; // 游离对象
if (N > 0 && N == a.length / 4) {
resize(a.length/2);
}
return item;
}
public Iterator<Item> iterator() {
return new ReverseArrayIterator();
}
private class ReverseArrayIterator implements Iterator<Item> {
private int i = N;
public boolean hasNext() { return i > 0; }
public Item next() {return a[--i];}
public void remove() {}
}
}下压栈(链表实现)
/**
* 下压栈(链表实现)
* @param <Item>
*/
public class Stack<Item> {
private Node first;
private int N;
private class Node {
Item item;
Node next;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return first == null;
}
public int size() {
return N;
}
public void push(Item item) {
Node oldfirst = first;
first = new Node();
first.item = item;
first.next = oldfirst;
N++;
}
}队列
/**
* 队列
* @param <Item>
*/
public class Queue<Item> {
private Node first;
private Node last;
private int N;
private class Node {
Item item;
Node next;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return first == null;
}
public int size() {
return N;
}
public void enqueue(Item item) {
Node oldlast = last;
last = new Node();
last.item = item;
last.next = null;
if (isEmpty()) {
first = last;
} else {
oldlast.next = last;
}
N++;
}
public Item dequeue() {
Item item = first.item;
first = first.next;
if (isEmpty()) {
last = null;
}
N--;
return item;
}
}优先队列
/**
* 优先队列模板
* 时间复杂度:
* 1、无序数组 插入:1 删除最大元素:N
* 2、有序数组 插入:M 删除最大元素:1
* 3、链表 插入:NlogN 删除最大元素:NlogN
* @param <Key>
*/
public class MaxPQExample<Key extends Comparable<Key>> {
public MaxPQExample() {
}
/**
* 创建初始容量为max的优先队列
* @param max
*/
public MaxPQExample(int max) {
}
/**
* 用a中的元素创建优先队列
* @param a
*/
public MaxPQExample(Key[] a) {
}
/**
* 插入元素
* @param v
*/
public void insert(Key v) {
}
/**
* 删除元素
* @return
*/
public Key delMax() {
return null;
}
/**
* 是否为空
* @return
*/
public boolean isEmpty() {
return false;
}
/**
* 返回最大元素
* @return
*/
public Key max() {
return null;
}
/**
* 返回元素个数
* @return
*/
public int size() {
return 0;
}
}二分二叉树
/**
* 二分二叉树
* 构造说明:小于根节点放左边,大于根节点放右边
* 时间复杂度:随机构建的N个节点的二分二叉树,查找比较次数~2lgN
*/
public class BST<Key extends Comparable<Key>, Value> {
private Node root; // 二叉查找树的根结点
private class Node {
private Key key; // 键
private Value val; // 值
private Node left, right; // 指向子树的链接
private int N; // 以该结点为根的子树中的结点总数
public Node(Key key, Value val, int N) {
this.key = key;
this.val = val;
this.N = N;
}
}
public int size() {
return size(root);
}
private int size(Node x) {
if (x == null) return 0;
else return x.N;
}
public Value get(Key key) {
return get(root, key);
}
private Value get(Node x, Key key) { // 在以x为根结点的子树中查找并返回key所对应的值;
// 如果找不到则返回null
if (x == null) return null;
int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
if (cmp < 0) return get(x.left, key);
else if (cmp > 0) return get(x.right, key);
else return x.val;
}
public void put(Key key, Value val) { // 查找key,找到则更新它的值,否则为它创建一个新的结点
root = put(root, key, val);
}
private Node put(Node x, Key key, Value val) {
// 如果key存在于以x为根结点的子树中则更新它的值;
// 否则将以key和val为键值对的新结点插入到该子树中
if (x == null) return new Node(key, val, 1);
int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
if (cmp < 0) x.left = put(x.left, key, val);
else if (cmp > 0) x.right = put(x.right, key, val);
else x.val = val;
x.N = size(x.left) + size(x.right) + 1;
return x;
}
public Key max() {
return max(root).key;
}
private Node max(Node x) {
if (x.right == null) return x;
return max(x.right);
}
public Key min() {
return min(root).key;
}
private Node min(Node x) {
if (x.left == null) return x;
return min(x.left);
}
public Key floor(Key key) {
Node x = floor(root, key);
if (x == null) return null;
return x.key;
}
private Node floor(Node x, Key key) {
if (x == null) return null;
int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
if (cmp == 0) return x;
if (cmp < 0) return floor(x.left, key);
Node t = floor(x.right, key);
if (t != null) return t;
else return x;
}
public Key select(int k) {
return select(root, k).key;
}
private Node select(Node x, int k) { // 返回排名为k的结点
if (x == null) return null;
int t = size(x.left);
if (t > k) return select(x.left, k);
else if (t < k) return select(x.right, k - t - 1);
else return x;
}
public int rank(Key key) {
return rank(key, root);
}
private int rank(Key key, Node x) { // 返回以x为根结点的子树中小于x.key的键的数量
if (x == null) return 0;
int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
if (cmp < 0) return rank(key, x.left);
else if (cmp > 0) return 1 + size(x.left) + rank(key, x.right);
else return size(x.left);
}
public void deleteMin() {
root = deleteMin(root);
}
private Node deleteMin(Node x) {
if (x.left == null) return x.right;
x.left = deleteMin(x.left);
x.N = size(x.left) + size(x.right) + 1;
return x;
}
public void delete(Key key) {
root = delete(root, key);
}
private Node delete(Node x, Key key) {
if (x == null) return null;
int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
if (cmp < 0) x.left = delete(x.left, key);
else if (cmp > 0) x.right = delete(x.right, key);
else {
if (x.right == null) return x.left;
if (x.left == null) return x.right;
Node t = x;
x = min(t.right); // 请见算法3.3(续2)
x.right = deleteMin(t.right);
x.left = t.left;
}
x.N = size(x.left) + size(x.right) + 1;
return x;
}
public Iterable<Key> keys() {
return keys(min(), max());
}
public Iterable<Key> keys(Key lo, Key hi) {
Queue<Key> queue = new Queue<Key>();
keys(root, queue, lo, hi);
return queue;
}
private void keys(Node x, Queue<Key> queue, Key lo, Key hi) {
if (x == null) return;
int cmplo = lo.compareTo(x.key);
int cmphi = hi.compareTo(x.key);
if (cmplo < 0) keys(x.left, queue, lo, hi);
if (cmplo <= 0 && cmphi >= 0) queue.enqueue(x.key);
if (cmphi > 0) keys(x.right, queue, lo, hi);
}
// 请见算法3.3(续1)
// max()、min()、floor()、ceiling()方法请见算法3.3(续2)
// select()、rank()方法请见算法3.3(续3)
// delete()、deleteMin()、deleteMax()方法请见算法3.3(续4)
// keys()方法请见算法3.3(续5)
}平衡二叉树
/**
* 平衡二叉树
* 目标:N个节点的树,树高为lgN
* 1:2-3查找树
* 2:红黑查找树,两个 2- 表示 3- 的2-3查找树
*/
public class RedBlackBST<Key extends Comparable<Key>, Value> {
private static final boolean RED = true;
private static final boolean BLACK = false;
private Node root;
private class Node {
Key key;
Value val;
Node left, right;
int N;
boolean color;
Node(Key key, Value val, int N, boolean color) {
this.key = key;
this.val = val;
this.N = N;
this.color = color;
}
}
private boolean isRed(Node x) {
if (x == null) {
return false;
} else {
return x.color == RED;
}
}
/**
* 红左旋转
* @param h
* @return
*/
private Node rotateLeft(Node h) {
Node x = h.right;
h.right = x.left;
x.left = h;
x.color = h.color;
h.color = RED;
x.N = h.N;
h.N = 1 + size(h.left) + size(h.right);
return x;
}
/**
* 红佑旋转
* @param h
* @return
*/
private Node rotateRight(Node h) {
Node x = h.left;
h.left = x.right;
x.right = h;
x.color = h.color;
h.color = RED;
x.N = h.N;
h.N = 1 + size(h.left) + size(h.right);
return x;
}
/**
* 分割双红
* @param h
*/
private void flipColors(Node h) {
h.color = RED;
h.left.color = BLACK;
h.right.color = BLACK;
}
private int size() {
return size(root);
}
private int size(Node x) {
if (x == null) return 0;
else return x.N;
}
public void put(Key key, Value val) { // 查找key,找到则更新其值,否则为它新建一个结点
root = put(root, key, val);
root.color = BLACK;
}
private Node put(Node h, Key key, Value val) {
if (h == null) // 标准的插入操作,和父结点用红链接相连
return new Node(key, val, 1, RED);
int cmp = key.compareTo(h.key);
if (cmp < 0) h.left = put(h.left, key, val);
else if (cmp > 0) h.right = put(h.right, key, val);
else h.val = val;
if (isRed(h.right) && !isRed(h.left)) h = rotateLeft(h);
if (isRed(h.left) && isRed(h.left.left)) h = rotateRight(h);
if (isRed(h.left) && isRed(h.right)) flipColors(h);
h.N = size(h.left) + size(h.right) + 1;
return h;
}
}图
/**
* @author jinchenj
* @description 图:用临接表表达,程序用由顶点索引的整形链表数组表示
* @create:2024-12-1614:00:11
*/
public class Graph {
private final int V; // 顶点数目
private int E; // 边的数目
private Bag<Integer>[] adj; // 邻接表
/**
* 创建一个含有 个顶点但不含有边的图
* @param V
*/
Graph(int V) {
this.V = V;
this.E = 0;
adj = (Bag<Integer>[]) new Bag[V]; // 创建邻接表
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) // 将所有链表初始化为空
adj[v] = new Bag<Integer>();
}
/**
* 从标准输入流 in 读入一幅图
* @param in
*/
Graph(In in) {
this(in.readInt()); // 读取V并将图初始化
int E = in.readInt(); // 读取E
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++)
{ // 添加一条边
int v = in.readInt(); // 读取一个顶点
int w = in.readInt(); // 读取另一个顶点
addEdge(v, w); // 添加一条连接它们的边
}
}
/**
* 顶点数
* @return
*/
int V() {
return V;
}
/**
* 边数
* @return
*/
int E() {
return E;
}
/**
* 向图中添加一条边 v-w
* @param v
* @param w
*/
public void addEdge(int v, int w) {
adj[v].add(w); // 将w添加到v的链表中
adj[w].add(v); // 将v添加到w的链表中
E++;
}
/**
* 和 v 相邻的所有顶点
* @param v
* @return
*/
Iterable<Integer> adj(int v) {
return adj[v];
}
public String toString() {
return null;
}
}应用数据结构
自定义计时器
/**
* 自定义计时器
*/
public class StopWatch {
private final long start;
public StopWatch() {
start = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
public String getStart() {
String startStr = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss").format(new Date(start));
return startStr;
}
public double elapsedTime () {
long now = System.currentTimeMillis();
return (now - start) / 1000.0;
}
}可视化累加器
/**
* 可视化累加器
*/
public class VisualAccumlator {
private double x;
private int n;
private double sum;
private double pow2sum;
public VisualAccumlator(int trials, double max) {
StdDraw.setXscale(0, trials);
StdDraw.setYscale(0, max);
StdDraw.setPenRadius(0.005);
}
public void addDataValue (double in) {
x = in;
n++;
sum();
pow2sum();
StdDraw.setPenColor(StdDraw.DARK_GRAY);
StdDraw.point(n, x);
StdDraw.setPenColor(StdDraw.YELLOW);
StdDraw.point(n, sum);
StdDraw.setPenColor(StdDraw.RED);
StdDraw.point(n, mean() * 1000);
StdDraw.setPenColor(StdDraw.BLUE);
StdDraw.point(n, stddev() * 1000);
}
/**
* 和
* @return
*/
public double sum () {
sum += x;
return sum;
}
/**
* 平方和
* @return
*/
public double pow2sum() {
pow2sum = Math.pow(x - mean(), 2);
return pow2sum;
}
/**
* 期望
* @return
*/
public double mean () {
double mean = BigDecimal.valueOf(sum).divide(BigDecimal.valueOf(n), 2).doubleValue();
return mean;
}
/**
* 标准差
* @return
*/
public double var () {
double var = pow2sum/n;
return var;
}
/**
* 方差
* @return
*/
public double stddev () {
return Math.sqrt(this.var());
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "VisualAccumlator{" +
"x=" + x +
", n=" + n +
", sum=" + sum +
", pow2sum=" + pow2sum +
'}';
}
}算法
查找
二分法查找
/**
* 二分法查找
* 时间复杂度:O(log2n)
*/
public class BinarySearch {
private int[] a;
public BinarySearch(int[] keys) {
a = new int[keys.length];
for (int i = 0; i < keys.length; i++) {
a[i] = keys[i]; // 保护性复制
}
Arrays.sort(a);
}
public boolean contains(int key) {
return rank(key) != -1;
}
/**
* 二分法
* @param key
* @return
*/
private int rank(int key) {
int lo = 0; // 小索引
int hi = a.length - 1; // 大索引
while (lo <= hi) {
int mid = lo + (hi - lo) / 2; // 中间索引
if (key < a[mid]) {
hi = mid - 1;
} else if (key > a[mid]) {
lo = mid + 1;
} else {
return mid;
}
}
return -1;
}
}二分查找
- 时间复杂度:O(log2n)
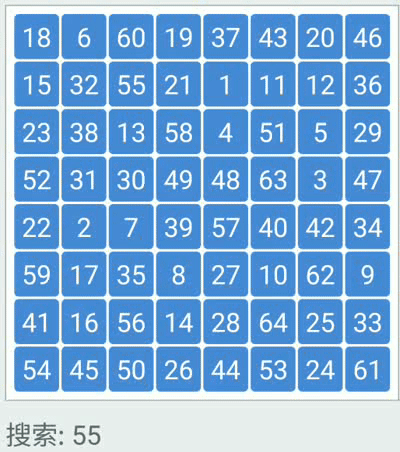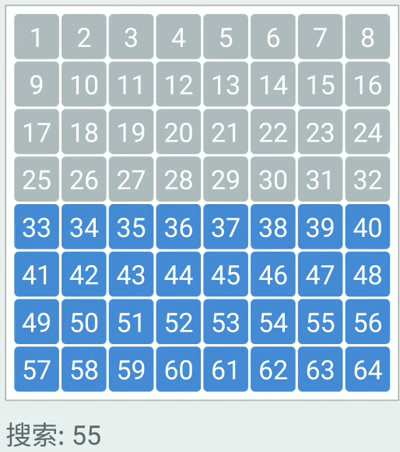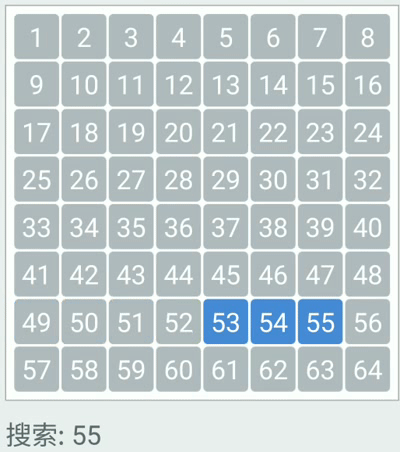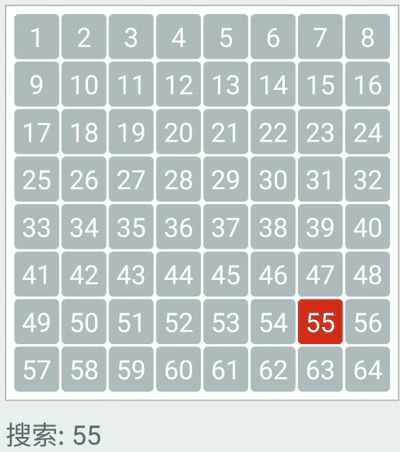
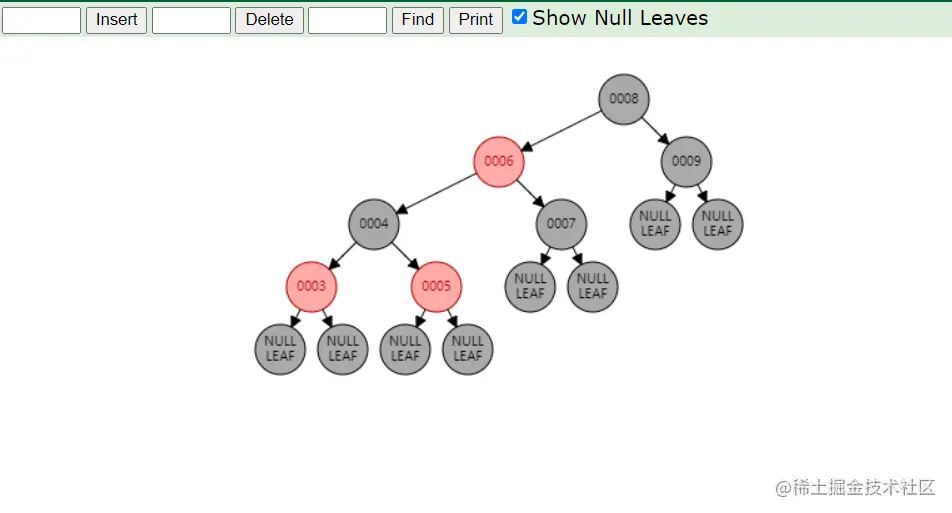
二叉查找树(BST)
- 时间复杂度:
- 查找:平均时间复杂度为 O(log N),最坏情况下为 O(N)(当树退化为链表时)。
- 插入:平均时间复杂度为 O(log N),最坏情况下为 O(N)。
- 删除:平均时间复杂度为 O(log N),最坏情况下为 O(N)
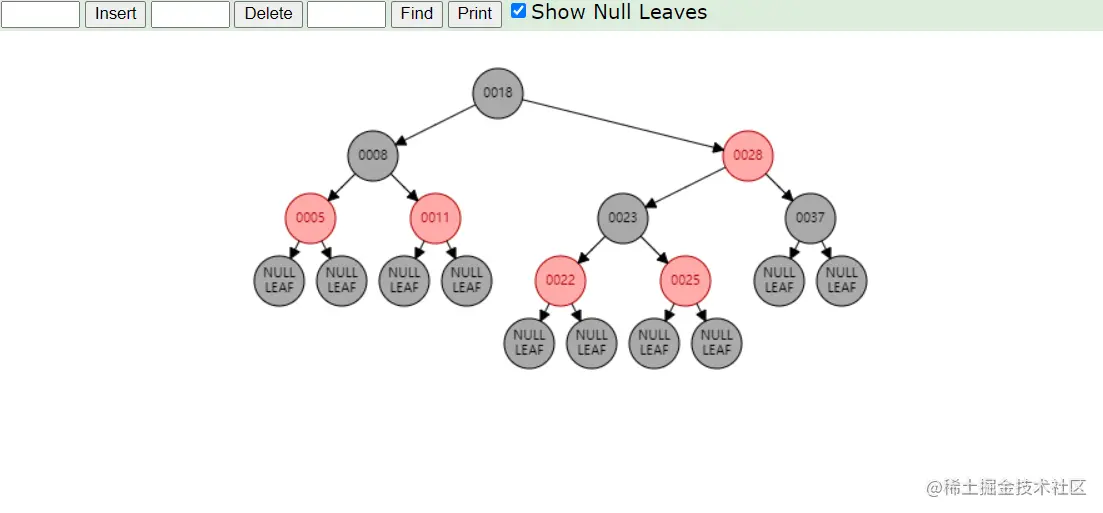
红黑树
- 时间复杂度:
- 查找:平均时间复杂度为 O(log N)
- 插入:平均时间复杂度为 O(log N)
- 删除:平均时间复杂度为 O(log N)
排序
选择排序
/**
* 选择排序:第i个元素和剩余元素比较选出最小的
* 时间复杂度:上下界 n^2,N^2/2次比较,N次交换,幂函数增长
* 空间复杂度:原地排序算法
*/
public class Selection {
/**
* 排序
* @param a
*/
public static void sort(Comparable[] a) {
int N = a.length;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
int min = i;
for (int j = i+1; j < N; j++) {
if (less(a[j], a[min])) {
min = j;
}
}
exch(a, i, min);
}
}
/**
* 判断大小
* @param v
* @param w
* @return
*/
private static boolean less(Comparable v, Comparable w) {
return v.compareTo(w) < 0;
}
/**
* 交换元素
* @param a
* @param i
* @param j
*/
private static void exch(Comparable[] a, int i, int j) {
Comparable t = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = t;
}
/**
* 打印数组
* @param a
*/
private static void show(Comparable[] a) {
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
StdOut.print(a[i] + " ");
}
StdOut.println();
}
/**
* 测试数组是否有顺序
* @param a
* @return
*/
private static boolean isSorted(Comparable[] a) {
for (int i = 1; i < a.length; i++) {
if (less(a[i], a[i-1])) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String filePath = System.getProperty("user.dir") + "/src/txt/" + "Example.txt";
String[] a = In.readStrings(filePath);
sort(a);
StdOut.println("是否排序:" + isSorted(a));
show(a);
}
}插入排序
/**
* 插入排序:依次判相邻的元素中最小的
* 时间复杂度: 上下界 n^2,平均N^2/4次比较,N^2/4次交换,最坏N^2/2 次比较,N^2/2次交换,最好N-1次比较,0次交换
* 空间复杂度:原地排序算法
* 说明:和集合的初始状态关联性较大
*/
public class Insertion {
/**
* 排序
* @param a
*/
public static void sort(Comparable[] a) {
int N = a.length;
for (int i = 1; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = i; j >0 && less(a[j], a[j -1]); j--) {
exch(a, j, j-1);
}
}
}
/**
* 判断大小
* @param v
* @param w
* @return
*/
private static boolean less(Comparable v, Comparable w) {
return v.compareTo(w) < 0;
}
/**
* 交换元素
* @param a
* @param i
* @param j
*/
private static void exch(Comparable[] a, int i, int j) {
Comparable t = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = t;
}
/**
* 打印数组
* @param a
*/
private static void show(Comparable[] a) {
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
StdOut.print(a[i] + " ");
}
StdOut.println();
}
/**
* 测试数组是否有顺序
* @param a
* @return
*/
private static boolean isSorted(Comparable[] a) {
for (int i = 1; i < a.length; i++) {
if (less(a[i], a[i-1])) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String filePath = System.getProperty("user.dir") + "/src/txt/" + "Example.txt";
String[] a = In.readStrings(filePath);
sort(a);
StdOut.println("是否排序:" + isSorted(a));
show(a);
}
}希尔排序
/**
* 希尔排序:缩小增量的插入排序
* 时间复杂度:上界 n^(3/2)、下界 n*log2n
* 空间复杂度:原地排序算法
* 说明:在插入排序基础上新增增幅h的概念,大幅提高效率
*/
public class Shell {
/**
* 排序
* @param a
*/
public static void sort(Comparable[] a) {
int N = a.length;
int h = 1;
while (h < N/3) {
h = 3*h + 1;
}
while (h >= 1) {
for (int i = h; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = i; j >= h && less(a[j], a[j-h]); j -= h) {
exch(a, j, j-h);
}
}
h = h/3;
}
}
/**
* 判断大小
* @param v
* @param w
* @return
*/
private static boolean less(Comparable v, Comparable w) {
return v.compareTo(w) < 0;
}
/**
* 交换元素
* @param a
* @param i
* @param j
*/
private static void exch(Comparable[] a, int i, int j) {
Comparable t = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = t;
}
/**
* 打印数组
* @param a
*/
private static void show(Comparable[] a) {
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
StdOut.print(a[i] + " ");
}
StdOut.println();
}
/**
* 测试数组是否有顺序
* @param a
* @return
*/
private static boolean isSorted(Comparable[] a) {
for (int i = 1; i < a.length; i++) {
if (less(a[i], a[i-1])) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String filePath = System.getProperty("user.dir") + "/src/txt/" + "Example.txt";
String[] a = In.readStrings(filePath);
sort(a);
StdOut.println("是否排序:" + isSorted(a));
show(a);
}
}并归排序
/**
* 并归排序
* 时间复杂度:NlogN
* 空间复杂度:N
* 说明:
*/
public class Merge {
private static Comparable[] aux; // 辅助数组
/**
* 原地并归:将a[lo..mid] 和 a[mid+1..hi] 归并
* @param a
* @param lo
* @param mid
* @param hi
*/
private static void merge(Comparable[] a, int lo, int mid, int hi) {
int i = lo;
int j = mid + 1;
for (int k = lo; k <= hi; k++) {
aux[k] = a[k];
}
for (int k = lo; k <= hi; k++) {
if (i > mid) {
a[k] = aux[j++];
} else if (j > hi) {
a[k] = aux[i++];
} else if (less(aux[j], aux[i])) {
a[k] = aux[j++];
} else {
a[k] = aux[i++];
}
}
}
/**
* 自上向下的并归排序
* @param a
* @param lo
* @param hi
*/
private static void sort(Comparable[] a, int lo, int hi) {
if (hi <= lo) {
return;
}
int mid = lo + (hi - lo) / 2;
sort(a, lo, mid);
sort(a, mid+1, hi);
merge(a, lo, mid, hi);
}
/**
* 排序
* @param a
*/
public static void sort(Comparable[] a) {
aux = new Comparable[a.length];
sort(a, 0, a.length - 1);
}
/**
* 判断大小
* @param v
* @param w
* @return
*/
private static boolean less(Comparable v, Comparable w) {
return v.compareTo(w) < 0;
}
/**
* 交换元素
* @param a
* @param i
* @param j
*/
private static void exch(Comparable[] a, int i, int j) {
Comparable t = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = t;
}
/**
* 打印数组
* @param a
*/
private static void show(Comparable[] a) {
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
StdOut.print(a[i] + " ");
}
StdOut.println();
}
/**
* 测试数组是否有顺序
* @param a
* @return
*/
private static boolean isSorted(Comparable[] a) {
for (int i = 1; i < a.length; i++) {
if (less(a[i], a[i-1])) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String filePath = System.getProperty("user.dir") + "/src/txt/" + "Example.txt";
String[] a = In.readStrings(filePath);
sort(a);
StdOut.println("是否排序:" + isSorted(a));
show(a);
}
}快速排序
/**
* 快速排序
* 时间复杂度:NlogN
* 空间复杂度:原地排序
* 说明:循环(按第一个元素切分,左侧是小的,右侧是大的),当两个指针相等时,排序完成。
*/
public class Quick {
/**
* 切分
* @param a
* @param lo
* @param hi
* @return
*/
private static int partition(Comparable[] a, int lo, int hi) {
int i = lo, j = hi + 1;
Comparable v = a[lo];
while (true) {
while (less(a[++i], v)) { // 比v小的数不做处理
if (i == hi) {
break;
}
}
while (less(v, a[--j])) { // 比v大的数不做处理
if (j == lo) {
break;
}
}
if (i >= j) { // 索引 i >= j,切分完成
break;
}
exch(a, i, j);
}
exch(a, lo, j);
return j;
}
/**
* 快速排序
*/
private static void sort(Comparable[] a, int lo, int hi) {
if (hi <= lo) {
return;
}
int j = partition(a, lo, hi);
sort(a, lo, j-1);
sort(a, j+1, hi);
}
/**
* 排序
* @param a
*/
public static void sort(Comparable[] a) {
StdRandom.shuffle(a);
sort(a, 0, a.length - 1);
}
/**
* 判断大小
* @param v
* @param w
* @return
*/
private static boolean less(Comparable v, Comparable w) {
return v.compareTo(w) < 0;
}
/**
* 交换元素
* @param a
* @param i
* @param j
*/
private static void exch(Comparable[] a, int i, int j) {
Comparable t = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = t;
}
/**
* 打印数组
* @param a
*/
private static void show(Comparable[] a) {
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
StdOut.print(a[i] + " ");
}
StdOut.println();
}
/**
* 测试数组是否有顺序
* @param a
* @return
*/
private static boolean isSorted(Comparable[] a) {
for (int i = 1; i < a.length; i++) {
if (less(a[i], a[i-1])) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String filePath = System.getProperty("user.dir") + "/src/txt/" + "Example.txt";
String[] a = In.readStrings(filePath);
sort(a);
StdOut.println("是否排序:" + isSorted(a));
show(a);
}
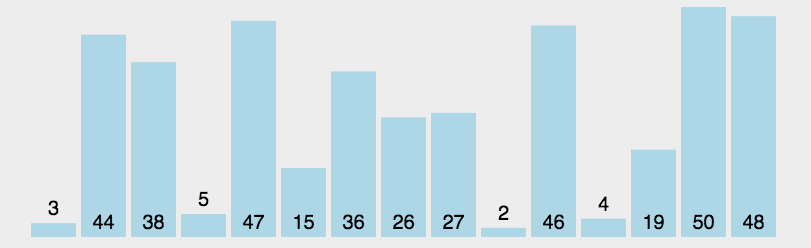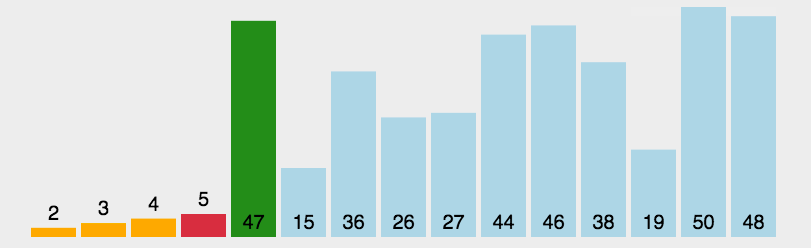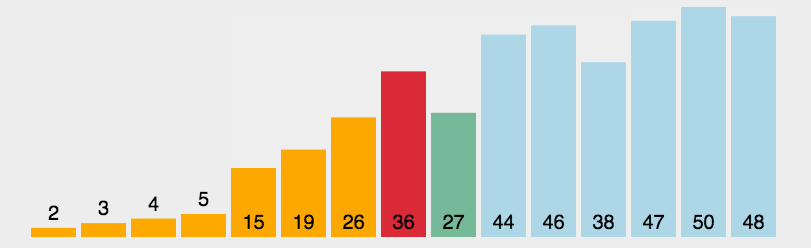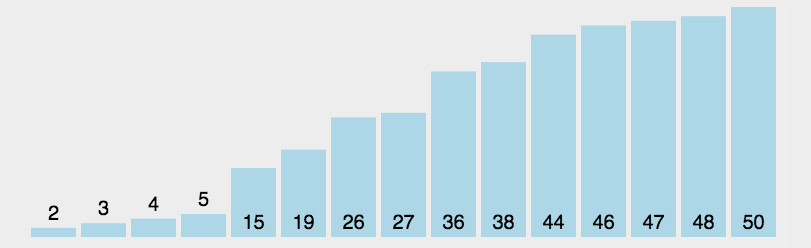
}选择排序
- 时间复杂度:O(n^2)
- 空间复杂度:O(1)
- 稳定性:不稳定
插入排序
- 时间复杂度:最坏 O(n2)、平均O(n2)、最好 O(n)
- 空间复杂度:O(1)
- 稳定性:不稳定

希尔排序
- 时间复杂度:最坏 O(n1.3)、平均O(n2)、最好 O(n)
- 空间复杂度:O(1)
- 稳定性:不稳定
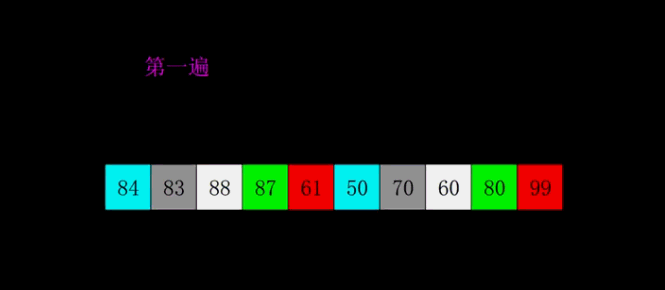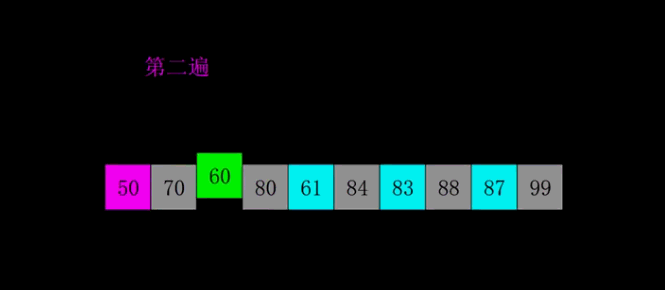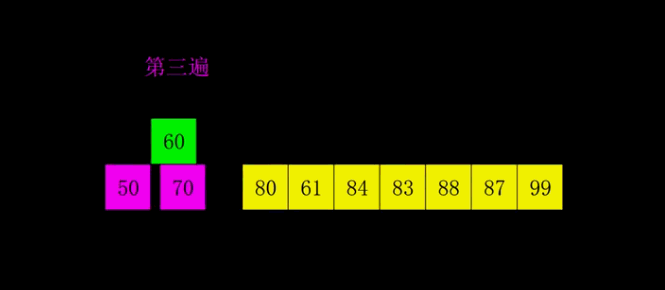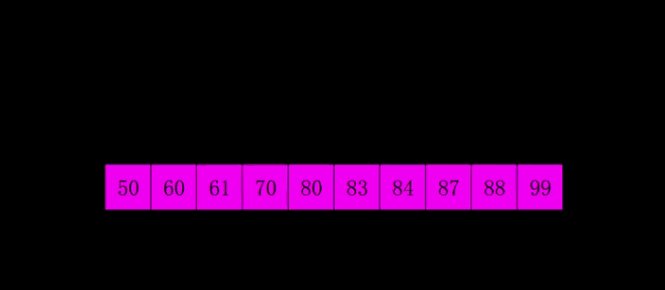
并归排序
- 时间复杂度:最坏 O(nlogn)、平均O(nlogn)、最好 O(nlogn)
- 空间复杂度:O(n)
- 稳定性:稳定
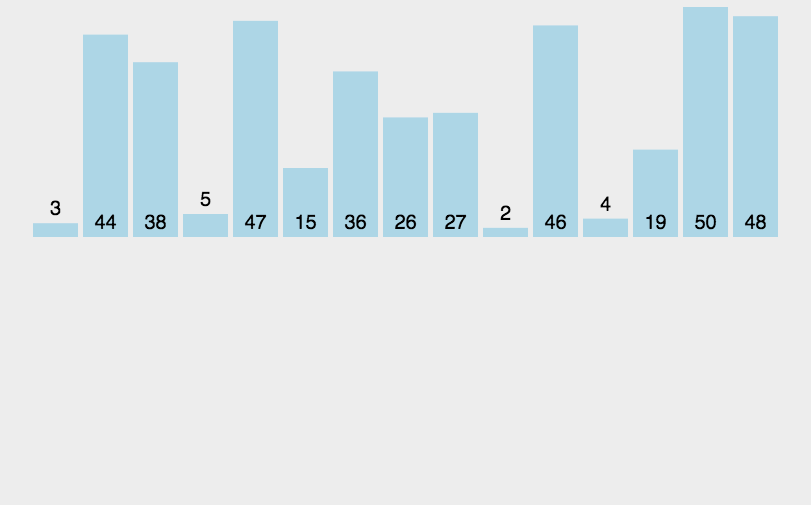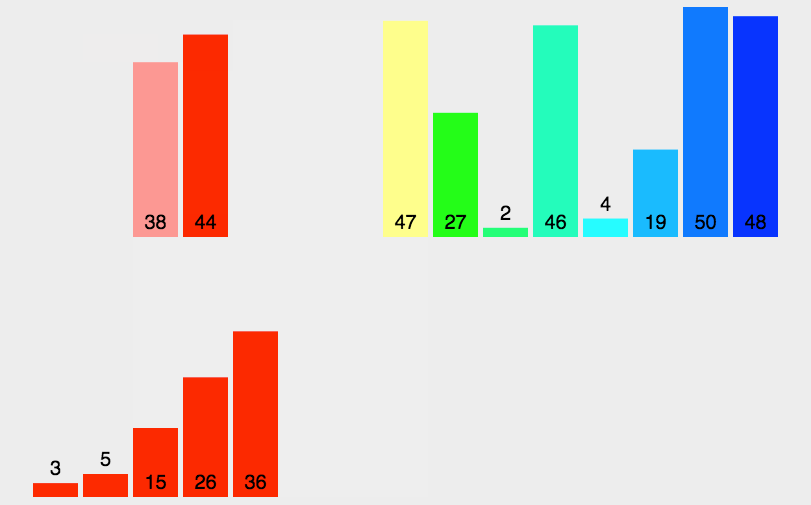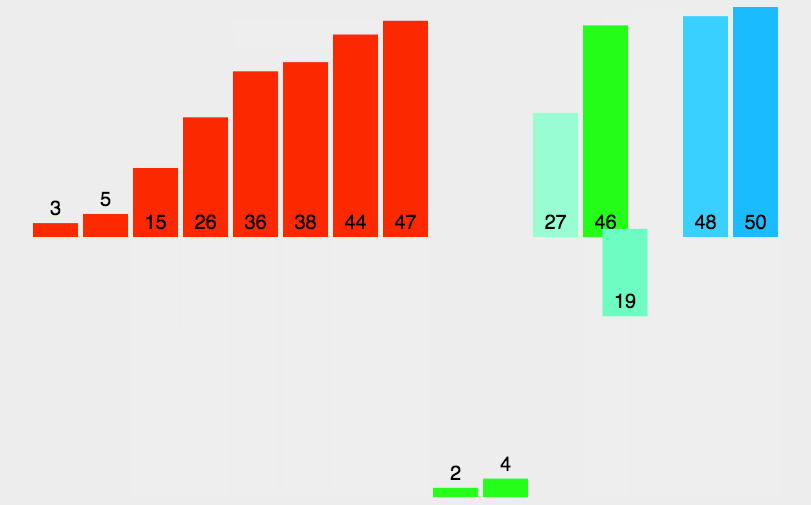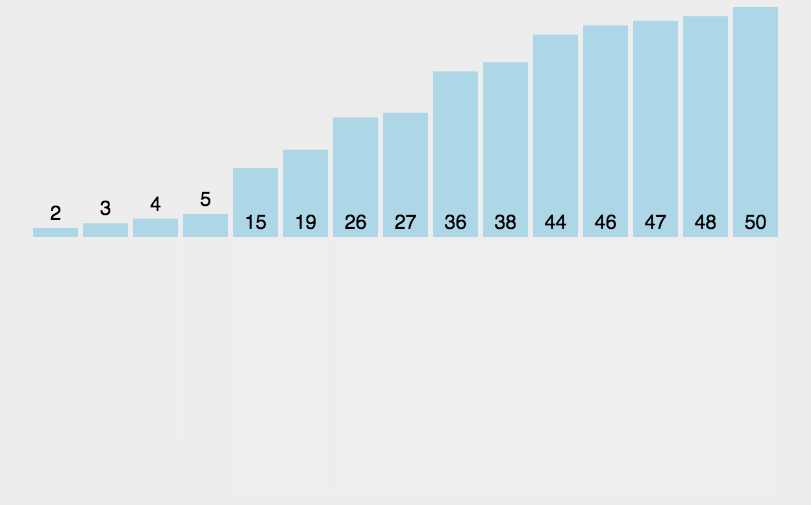
快速排序
- 时间复杂度:最坏 O(n^2)、平均O(nlogn)、最好 O(nlogn)
- 空间复杂度:O(nlogn)
- 稳定性:不稳定